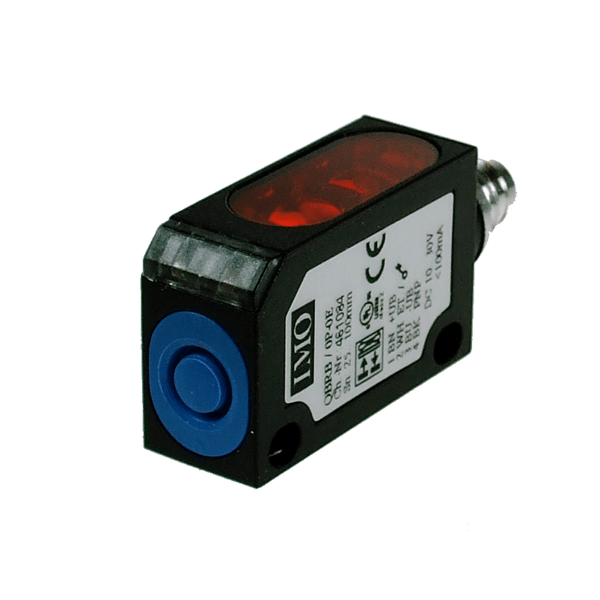
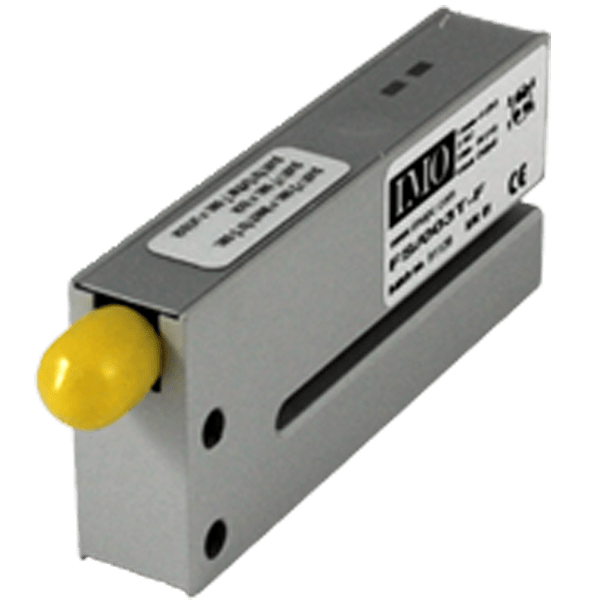
A photoelectric sensor enables to detect an element which goes through a light beam.
A photoelectric sensor is a sensor that enables to detect remotely.
There are several elements to take into account to choose a photoelectric sensor:
- The sensor range: in other words, the distance to which the sensor detects the object.
- The sensor supply voltage
- The sensor contact type (NO or NC) and the maximum power that runs in the dry contact. Attention, if the maximum intensity of the contact is not enough, you need to think about using a relay.
- Choosing the type of detection that you seek:
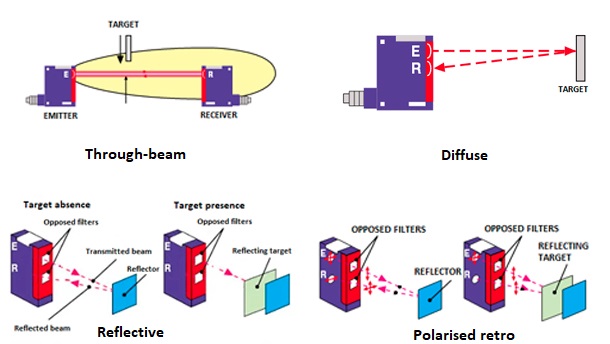
- through-beam: in this case, there are 2 sensors – one that emits the beam and one that receives the information. As soon as the receiver does not receive the beam anymore, then there is an object in the detection field.
- reflective: in this case, there is a reflector that sends back the beam to the sensor. As soon as an object passes between the sensor and the reflector, the beam is not sent back and there is detection.
- diffuse: if an object passes in the sensor light beam, the object sends back a part of the beam to the sensor which then detects the object.
- polarised retro: this solution is similar to the reflective one but enables to detect non-opaque objects.
- The type of sensor connection:
- wired
- with a M12 or M8 connection, in this case a specific cable is needed.
Sensor with connector

Sensor with cable
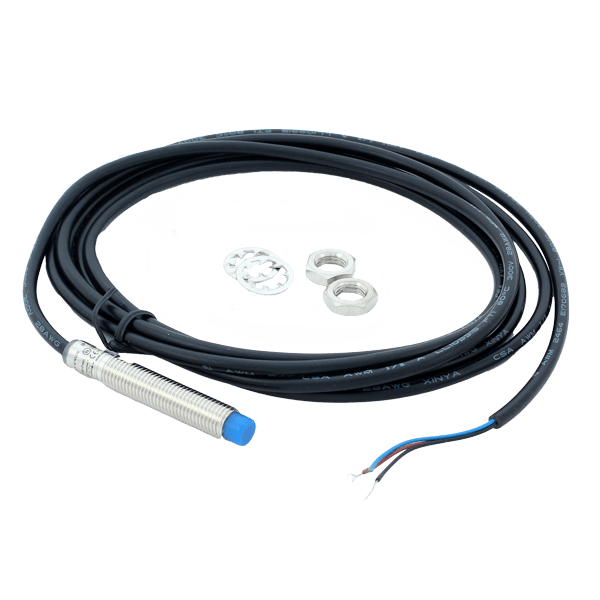

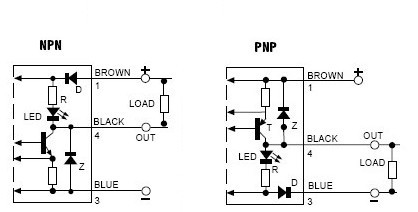
- Choosing the type of connection
- PNP Switched positive
- NPN Switched negative


 Blog
Blog



