What is the difference between Alternating and Direct current?
Direct current (DC)
It is an electric current in which electrons continously circulate in the same direction, that is to say from the negative pole to the positive pole. Its flow speed is of several metres per hour and its spread is as fast as the speed of light.

Alternating current (AC)
It is the other type of electric current. Electrons circulate alternatively in both directions in the circuit. In fact, it is the alternator rotation that generates back and forth movement for electrons. In this case, the movement of electrons is limited to a thousandth of a millimetre. Alternating current is measured by its frequency (in hertz). In Europe, the frequency is at 50Hz, the current then makes 50 back and forth movements per second.

Why favouring one type of current over another?
Alternating current is favoured for producing and transporting electrical energy for several reasons:
- An AC generator (synchronous or induction motor) is more efficient than a DC generator (DC machine). So, modern plants all produce alternating current.
- For the same power transported, line losses are lower with AC than with DC.
- We only know how to transform voltage in alternative efficiently. Yet, still to reduce energy losses in transportation, we transform current, at high voltage when leaving the plant (200,000V), at high voltage (60,000V), at medium voltage (20,000V) and finally at low voltage (220V in your plug or 380V three-phase.
In short, alternating current has only advantages for transportation and then is favoured for transporting energy.
However, we only know how to stock current in a battery, which restitutes direct current. Thus, for a machine operating with a battery, we would favour direct current.
DC is also favoured in electronics, especially because it enables a simple logic: voltage presence = positive information, voltage absence = negative information.
Which product to use for passing from AC to DC?
In an installation distributed by EDF (French multinational electric utility company), we have AC single phase or AC 3-phase 380V.
How to modify voltage in alternating?
To modify alternating voltage, we use a transformer:
- single-phase, which transforms the current in another voltage.
- three-phase, which modifies the 3 phases of 380V in 3 phases of another voltage.
With a transformer, it is possible to obtain the voltage you want. For instance, single-phase 220V to 18VAC if necessary. It is also important to be careful concerning the power required.


How to create a direct voltage from an alternating voltage?
In this case, several alternatives are possible:
- A power supply that transforms alternating (220V or 380V) in a direct voltage 12VDC, 24VDC or 48VDC. We can change the desired voltage by putting supplies in series. You need to choose right your power supply according to your need.


- A rectifier which enables to transform alternating current in another direct voltage.

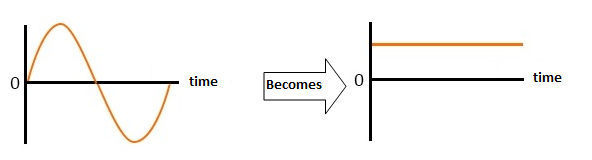
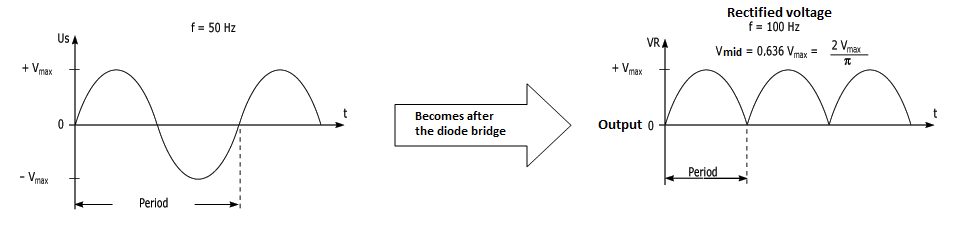
- A diode bridge which rectifies an alternating current to the correct voltage in a direct current. Hence, EASI-Spare suggests to see two different models: a classic bridge rectifier and a modular bridge rectifier.

How to size a diode bridge?
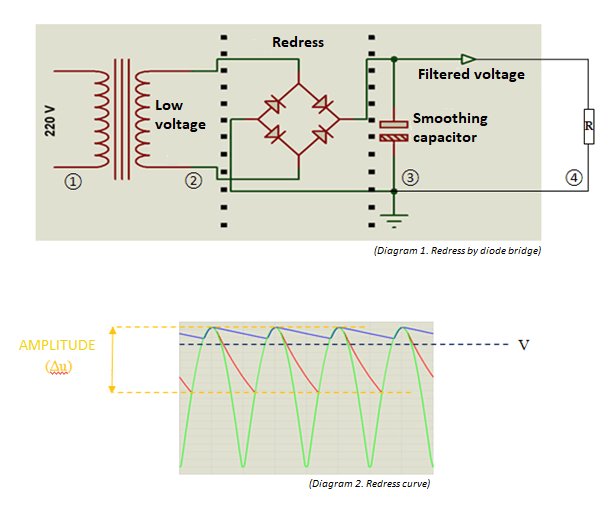
Dimensions:
Vmax = Utransfo x √2
Vmid = (2x Vmax)/π
Capacity capacitor:
C = I/(Δu x f)
With:
C = Capacity capacitor (F),
I = Current supposed constant (A),
Δu = Admissible waves (V),
f = Frequency (Hz).
Discharge resistance:
T=R x C
C = Capacity capacitor (F),
T = Discharge time constant (s),
R = Value of resistance (Ohm).

 Blog
Blog

